Polyamideimide (PAI) stands as the strongest polymer available today, boasting an exceptional tensile strength of 21,000 psi. When engineers select materials for critical industrial applications, understanding polymer mechanical properties becomes essential for ensuring operational safety and longevity. High-performance polymers like PEEK and Ultem offer impressive tensile strengths of 14,000 psi and 15,200 psi respectively, making them viable alternatives for demanding environments.
The mechanical properties of polymers have gained significant importance as these materials increasingly serve in structural applications, both independently and as matrix materials for composites. Additionally, most polymers exhibit time-dependent mechanical behavior, demonstrated through rate-dependent elastic moduli, yield strength, and post-yield characteristics. This time-dependent nature must be carefully considered when selecting the strongest plastic material for industrial use.
This article examines what truly defines polymer strength in industrial contexts and provides a comprehensive comparison of today’s strongest synthetic polymers. Furthermore, we’ll explore how thermal stability—with materials like PEEK withstanding temperatures up to 260°C and certain polyimide formulations exceeding 300°C—plays a crucial role in material selection for aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas applications.
Defining Strength in Industrial Polymers
Strength in industrial polymers encompasses multiple mechanical properties that determine performance under various loading conditions. Understanding these parameters is essential for selecting materials that can withstand specific industrial demands while maintaining dimensional stability. Engineers must consider several interrelated factors when evaluating polymer strength for critical applications.
Tensile strength vs compressive strength
Tensile strength measures a polymer’s ability to resist breaking under tension, calculated as the maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched before failure. In contrast to tensile forces, compressive strength quantifies a material’s capacity to withstand size reduction when subjected to load without fracturing. This fundamental difference exists because tensile stresses separate polymer atoms, while compressive forces bring them closer together.
When subjected to tensile forces, polymers initially undergo elastic deformation where they return to original dimensions upon stress removal. Subsequently, with increased force, they experience plastic deformation—a permanent, irreversible stretching. Tensile strength is typically expressed in Pascals (Pa), Megapascals (MPa), or pounds per square inch (psi).
Compressive strength values often differ significantly from tensile measurements for the same polymer. For instance, polyamide-imide exhibits compressive yield strength of 130 MPa, while polyimide reinforced with glass fiber reaches 220 MPa. These differences highlight why material selection must account for the primary stress type encountered in the application.
The mathematical relationship between stress and cross-sectional area is expressed as: σ = F/A where σ represents stress, F is the applied force, and A is the cross-sectional area. This equation applies to both tensile and compressive scenarios, though the direction of force differs.
Creep resistance and modulus explained
Creep resistance represents a critical property for industrial polymers used in structural applications, especially those subjected to constant loads at elevated temperatures. Creep is defined as the time-dependent deformation that occurs when a solid material is subjected to constant stress below its yield strength. For polymers especially, this phenomenon results from their inherent viscoelastic nature.
The creep process typically progresses through three distinct stages:
- Primary creep (Stage I): Characterized by decreasing creep rate as resistance to deformation increases
- Secondary creep (Stage II): Exhibits relatively constant creep rate and determines the time to failure
- Tertiary creep (Stage III): Shows accelerating deformation due to internal fracturing, leading to failure
Temperature significantly influences creep behavior in polymers. As temperature increases, chain mobility accelerates, resulting in greater creep deformation. One study observed that increasing temperature from 20°C to 50°C caused creep strain to increase 2.15 times, while at 80°C, the increase factor reached 3.93.
Material composition also affects creep resistance. Semi-crystalline polymers generally demonstrate better creep resistance than amorphous polymers because crystalline regions restrict molecular movement. Consequently, polymers with higher crystallinity percentages often exhibit superior dimensional stability under sustained loads.
Young’s modulus (elastic modulus) represents another critical strength parameter, defined as the ratio of stress to strain within a material’s proportional limit. Essentially, it measures a polymer’s stiffness—higher values indicate greater resistance to deformation under load. Modulus values for industrial polymers typically range from 0.7 GPa for HDPE to 12 GPa for glass-fiber reinforced polyimide.
How polymer stress-strain curves are interpreted
Stress-strain curves provide comprehensive insights into polymer mechanical behavior under applied forces. These graphs plot stress (force per unit area) against strain (extension per unit length) as a polymer undergoes deformation. For engineers, these curves reveal crucial information about elastic modulus, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and failure characteristics.
A typical polymer stress-strain curve exhibits several distinct regions:
- Linear elastic region: The initial straight-line portion where stress and strain are proportional according to Hooke’s Law. The slope of this line defines the Young’s modulus of elasticity.
- Yield point: Where the curve deviates from linearity, indicating the transition from elastic to plastic deformation. This represents the stress level at which permanent deformation begins.
- Strain hardening region: Beyond the yield point, where plastic deformation continues but requires increasing stress due to molecular realignment.
- Ultimate tensile strength: The maximum stress value on the curve, after which necking (localized narrowing) may occur.
- Fracture point: Where complete material failure occurs.
Different polymer types produce characteristically different curve shapes. Glassy or semi-crystalline polymers below their glass transition temperature typically show higher modulus values but limited elongation before failure. In contrast, elastomers or semi-crystalline polymers above their glass transition temperature demonstrate lower initial modulus but much greater elongation capacity.
The stress-strain relationship for polymers exhibits significant time and temperature dependence, distinguishing their behavior from other material classes. This viscoelastic nature explains why polymer performance under short-duration testing may not accurately predict long-term behavior under sustained loads—further emphasizing the importance of creep testing for industrial applications.
PEEK: A High-Performance Polymer for Harsh Environments
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) ranks among the most capable engineering thermoplastics available, defined by its remarkable mechanical stability in extreme environments. Unlike standard polymers, PEEK maintains its structural integrity under conditions that would rapidly degrade conventional materials.
PEEK polymer structure and semi-crystalline behavior
PEEK derives its exceptional properties from its unique molecular architecture—a rigid aromatic backbone composed of repeated units featuring one ketone bond and two ether bonds in an aromatic ring. This chemical structure creates inherent stiffness at the molecular level, contributing to its impressive thermal and mechanical performance.
As a semi-crystalline thermoplastic, PEEK contains both ordered crystalline regions and disordered amorphous zones. The crystalline domains provide strength and chemical resistance, whereas the amorphous regions contribute to toughness and flexibility. Processing conditions significantly influence the final crystallinity level, which can reach up to 48% maximum achievable crystallinity. Higher crystallinity typically results in greater strength and chemical resistance at the expense of some impact resistance.
The semi-crystalline nature gives PEEK excellent wear resistance, dimensional stability, and fatigue resistance—properties that remain largely intact even at elevated temperatures. Moreover, PEEK’s crystalline structure contributes significantly to its exceptional creep resistance, allowing it to withstand sustained loads without permanent deformation.
Tensile strength: 14,000 psi
PEEK exhibits impressive tensile strength of 14,000 psi (90-100 MPa) in its unfilled form, positioning it among the strongest thermoplastic polymers commercially available. This strength level allows PEEK components to replace metal parts in numerous applications while providing substantial weight reduction.
The material demonstrates an elastic modulus of 3.6 GPa, indicating excellent stiffness under load. Indeed, PEEK’s mechanical profile extends beyond mere tensile strength—its flexural strength reaches approximately 25,000 psi (165 MPa), providing exceptional resistance to bending forces.
For applications requiring even greater mechanical performance, carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK grades can achieve tensile strengths of 29,000 psi while maintaining properties at temperatures as high as 299°C. These enhanced formulations offer strength-to-weight ratios that outperform many metals and alloys.
Thermal resistance up to 480ºF
PEEK’s exceptional thermal stability sets it apart from most engineering polymers. The material features a glass transition temperature of approximately 143°C (289°F) and melts around 343°C (649°F). In practical applications, PEEK maintains its mechanical properties at continuous operating temperatures up to 480°F (250°C).
In fact, PEEK can function in steam or high-pressure water environments for thousands of hours at temperatures of 480°F with no significant degradation of properties. This remarkable thermal resilience results from the strong chemical bonds in its aromatic backbone structure.
The material’s thermal durability is complemented by excellent flame resistance. PEEK achieves a UL94 V-0 flammability rating, indicating it resists combustion up to nearly 600°C and produces minimal smoke or toxic emissions when exposed to flame.
Applications in aerospace and oil & gas
In aerospace applications, PEEK’s combination of light weight, high strength, and temperature resistance makes it ideal for replacing metal components. The material finds use in structural brackets, interior components, and applications where weight reduction and flame resistance are critical. As one aerospace industry application highlights, “PEEK polymer has been specified for aircraft landing gear hubcaps withstanding impacts of flying debris and has excellent environmental resistance in harsh conditions”.
Within the oil and gas industry, PEEK excels in extreme downhole environments where temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposure would destroy conventional materials. Applications include:
- Sealing systems and face seals at wellheads containing high-pressure production fluids and gasses
- Bearing components that benefit from PEEK’s self-lubricating properties
- Valve plates, rings, piston rings, and rod packing in reciprocating compressors
- Labyrinth seals and downhole electrical connectors
PEEK’s combination of properties—including chemical resistance to sour gas environments, excellent wear characteristics, and thermal stability—makes it particularly valuable in these demanding applications. Its ability to maintain structural integrity while resisting corrosion offers significant advantages over traditional metal components in hostile oil field environments.
Torlon (PAI): The Strongest Unfilled Thermoplastic
Torlon (polyamide-imide) stands in a class of its own among engineering thermoplastics, transitioning from thermoplastic to thermoset during post-processing. First and foremost, this unique chemical transformation gives Torlon exceptional mechanical properties that surpass virtually all other melt-processable polymers, making it the material of choice for the most demanding industrial applications.
Tensile strength: 21,000 psi
Torlon PAI boasts the highest tensile strength of any unreinforced thermoplastic at 21,000 psi, establishing it as the strongest polymer available for industrial applications. This exceptional strength results from its molecular structure and the post-curing process that increases molecular weight through chain extension. Alongside impressive tensile properties, Torlon demonstrates remarkable compressive strength exceeding 35,000 psi, far surpassing most engineering plastics.
Notably, Torlon retains its mechanical integrity at extreme temperatures, maintaining functional properties at continuous operating temperatures up to 500°F (260°C). Its heat deflection temperature significantly exceeds that of PEEK, allowing Torlon to retain higher strength and stiffness at elevated temperatures. Despite these high-temperature capabilities, Torlon performs admirably in cryogenic conditions without becoming brittle, offering truly versatile performance across temperature extremes.
The post-curing process dramatically transforms Torlon’s properties, increasing elongation from approximately 5% to 15%. This significant improvement in toughness occurs without sacrificing strength, yielding a material that combines rigidity with impact resistance.
Excellent wear and radiation resistance
Torlon exhibits superior tribological properties that make it exceptionally suitable for wear applications. In particular, wear-resistant grades offer excellent performance under both high velocity and high pressure conditions, often eliminating the need for lubrication. As a result, Torlon excels in applications requiring:
- Bearings and seal rings in harsh environments
- Valve seats and piston rings in high-performance engines
- Precision gears for aerospace applications
- Compressor components in oil and gas equipment
PAI polymers demonstrate outstanding radiation resistance, significantly outperforming many other engineering plastics when exposed to high levels of radiation. This property proves invaluable for components in nuclear power installations and space applications. Yet another advantage is Torlon’s exceptional chemical resistance to strong acids, most organic compounds, and aviation and automotive fluids, allowing it to function reliably in chemically aggressive environments.
Limitations: brittleness and cost
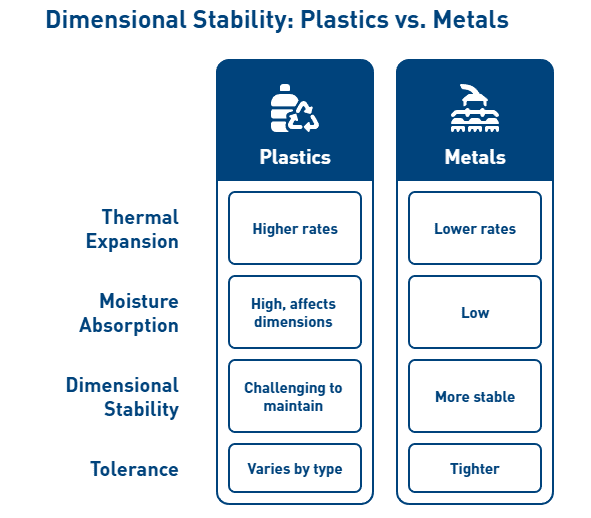
Nevertheless, Torlon has several limitations that engineers must consider. The material absorbs moisture, which can affect dimensional stability in applications lacking proper humidity control[152]. This moisture absorption becomes particularly concerning for precision components with tight tolerances.
Although post-curing improves toughness, fully cured Torlon cannot be recycled, presenting both economic and environmental challenges. In addition to recycling limitations, Torlon exhibits sensitivity to thermal shock when subjected to sudden high-temperature exposures.
Overall, Torlon typically commands a higher price than other high-performance polymers like PEEK[152]. This cost premium results from its specialized manufacturing processes and unique material properties. Despite the higher investment, many engineers find the cost justified for mission-critical components where performance at temperature extremes and under mechanical stress is essential.
Torlon’s distinctive combination of strength, temperature resistance, and wear properties continues to make it invaluable for applications where other polymers would fail, particularly in aerospace, automotive transmissions, and oil and gas equipment[173] where reliability under extreme conditions is paramount.
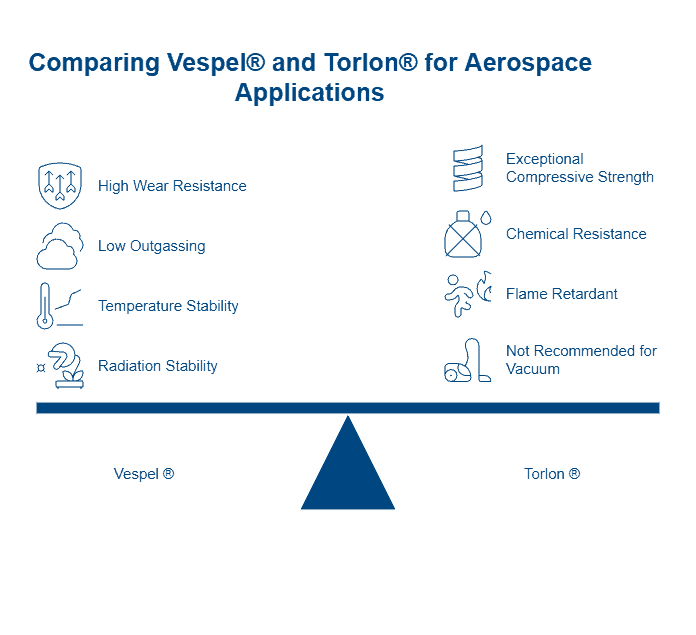
Vespel (Polyimide): Superior Creep and Wear Resistance
Vespel stands out among high-performance polymers as a premier polyimide material, renowned for its unmatched combination of thermal stability and mechanical strength in extreme environments. Since its introduction in 1965, this remarkable polymer has established itself as the material of choice for applications where other polymers reach their operational limits.
High-temperature stability beyond 300ºC
Vespel delivers exceptional thermal performance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures ranging from cryogenic conditions to over 300°C (570°F). For short-term exposure, certain grades can withstand temperatures up to 400°C, with potential to handle up to 538°C (1,000°F) in inert environments. This extraordinary thermal stability stems from Vespel’s unique polyimide molecular structure, which features imide linkages providing dimensional stability even under extreme heat.
Comparatively, Vespel exhibits the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion among unfilled plastics, making it ideal for precision components that must maintain tight tolerances across wide temperature fluctuations. This property, coupled with its outstanding creep characteristics, enables parts machined from Vespel to maintain dimensional stability under sustained loads at elevated temperatures.
Low coefficient of friction in dry environments
Vespel specifically excels in tribological applications, offering self-lubricating properties that eliminate the maintenance requirements typically associated with metal components. Different grades provide varying levels of friction performance:
- SP-1: The original unfilled grade offering superior wear resistance and insulation properties
- SP-3: Formulated for vacuum and dry environments with remarkably low outgassing
- SP-21: Graphite-enhanced grade with improved low-friction properties, functioning effectively with or without lubrication
- SP-211: Features a lower coefficient of friction than SP-21, incorporating PTFE to further reduce friction even in unlubricated conditions
Vespel’s ductility simultaneously contributes to its excellent sealing capabilities, primarily valuable in valve components where sealing against high-pressure fluids is critical. The polymer’s combination of low friction and exceptional wear resistance results in components that operate reliably for extended periods without lubrication, a significant advantage in environments where lubricants would degrade or contaminate processes.
Ideal for aerospace and semiconductor use
Aerospace engineers have embraced Vespel for its unique performance characteristics in critical applications. The material serves admirably in components such as locking elements for fasteners, valve seats and seals, thermal isolators, bearings, bushings, and splines. Its lightweight construction compared to metals offers substantial weight savings without compromising performance.
In semiconductor manufacturing, Vespel’s high purity and minimal outgassing properties prove invaluable. The SP-3 grade, furthermore, demonstrates superior performance in vacuum environments where contamination must be strictly controlled. The material’s electrical insulation properties coupled with its dimensional stability make it ideal for chip test sockets, wafer clamping rings, and high-temperature substrate handling.
Vespel’s exceptional creep and stress relaxation behavior outperforms virtually all other polymers, enabling it to maintain sealing force in high-pressure applications over extended periods. This characteristic, along with its ability to operate in extreme temperature environments, positions Vespel as an indispensable material for industries where failure is not an option.
Ultem (PEI): Balanced Strength and Machinability
Ultem (polyetherimide or PEI) represents an optimal balance between mechanical performance and processing capability, making it a versatile choice for demanding industrial applications. As an amorphous thermoplastic, Ultem offers a unique combination of properties that position it strategically between standard engineering plastics and ultra-high-performance polymers like PEEK and Torlon.
Tensile strength: 15,200 psi
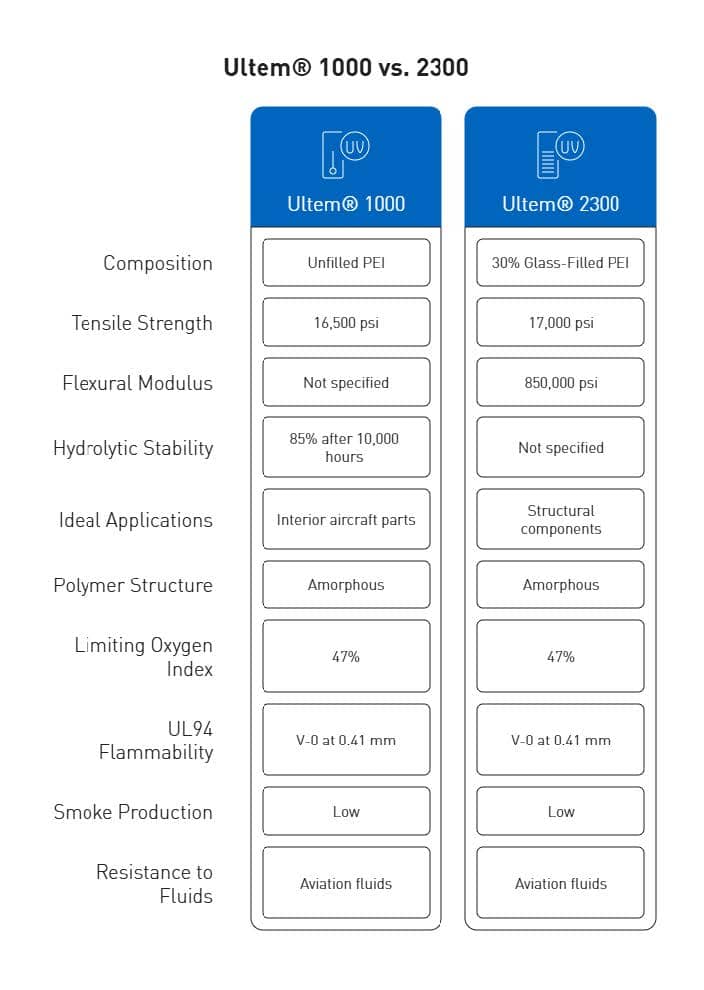
Ultem demonstrates impressive mechanical integrity with a tensile strength of 15,200 psi (105 MPa) in its unfilled grade. This strength level exceeds many standard engineering thermoplastics while providing excellent dimensional stability under load. The material’s mechanical profile extends beyond tensile properties, featuring flexural strength of 20,000 psi and compressive strength reaching 22,000 psi in unfilled grades.
For applications requiring enhanced structural performance, glass-fiber reinforced variants offer substantially improved properties. The Ultem 2000 series includes formulations with various glass fiber contents:
- Ultem 2100 (10% glass): 16,800 psi tensile strength
- Ultem 2200 (20% glass): 16,900 psi tensile strength
- Ultem 2300 (30% glass): 17,000 psi tensile strength
Correspondingly, these reinforced grades exhibit markedly improved flexural strength up to 27,000 psi and compressive strength reaching 32,000 psi. The glass reinforcement primarily enhances rigidity and dimensional stability while maintaining many beneficial characteristics of the base polymer.
High dielectric strength and chemical resistance
Historically, Ultem has been recognized for possessing the highest dielectric strength of any commercially available thermoplastic, measured at 830 V/mil according to ASTM D149. This exceptional electrical insulation capability makes Ultem particularly valuable for circuit boards, high-temperature lighting, electrical connectors, and electronic housings.
Regarding chemical stability, Ultem excels in hot water and steam environments—a distinguishing characteristic among high-performance polymers. The material retains 100% of its tensile strength after 2,000 steam autoclave cycles at 270°F and maintains 85% of tensile strength even after 10,000 hours of immersion in boiling water. Forthwith, this extraordinary hydrolysis resistance makes Ultem suitable for medical devices requiring repeated sterilization and food processing equipment exposed to high-temperature cleaning protocols.
Ultem’s chemical resistance extends to acids, oils, fats, and alcohols, along with exceptional flame resistance without requiring additives. It achieves a UL94 V-0 flammability rating and exhibits a high limiting oxygen index (LOI) of 47%, generating minimal smoke during combustion.
Cost-effective alternative to PEEK
While PEEK offers slightly superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, Ultem provides an economical alternative at approximately one-third the cost. This substantial price difference makes Ultem attractive for applications where PEEK’s extreme properties exceed requirements.
From a processing perspective, Ultem demonstrates excellent machinability compared to PEEK. The material allows for more efficient machining under similar conditions due to its slightly lower strength and reduced tool wear. This processing advantage translates to lower manufacturing costs for precision components while still delivering exceptional performance characteristics.
Ultem’s balanced property profile makes it suitable for diverse applications including aircraft interior components (meeting FAA regulation 25.853 for flammability), medical devices requiring sterilization, automotive electrical systems, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment. For precision machined components requiring tight tolerances, Ultem offers predictable dimensional stability across wide temperature ranges, making it ideal for high-precision industrial parts.
PPS: Chemically Resistant and Thermally Stable
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) occupies a strategic position among high-performance polymers, offering an exceptional balance of thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength at a moderate price point. With its aromatic rings linked by sulfur atoms, PPS delivers performance capabilities that make it suitable for demanding industrial applications where both chemical exposure and elevated temperatures are concerns.
Tensile strength: 12,500 psi
PPS exhibits impressive tensile strength of 12,500 psi (86 MPa) in its standard formulation, positioning it as the fourth strongest high-performance thermoplastic in unfilled form. For applications requiring enhanced mechanical properties, glass-fiber-reinforced variants achieve tensile strengths up to 17,500 psi, significantly expanding its performance envelope. The material’s compressive strength reaches approximately 21,500 PSI according to ASTM D695 testing, making it suitable for load-bearing components in industrial settings.
Beyond pure strength values, PPS demonstrates excellent rigidity and creep resistance under sustained loads, maintaining its mechanical integrity even at elevated temperatures. This characteristic makes it ideal for precision components that must retain their dimensions under mechanical stress. Among its mechanical attributes, PPS offers:
- High modulus and exceptional creep resistance
- Outstanding stress cracking resistance
- Excellent abrasion resistance and wear properties
These mechanical properties remain largely intact across PPS’s broad operating temperature range, contributing to its reliability in structurally demanding applications.
Excellent dimensional stability and flame retardance
PPS maintains dimensional stability under conditions that would cause significant deformation in conventional polymers. The material exhibits remarkable thermal properties with a melting temperature of 280°C (540°F) and continuous service capability up to 200°C (392°F) with short-term resistance to temperatures as high as 260°C (500°F).
Equally important, PPS demonstrates minimal water absorption below 0.1%, allowing it to maintain dimensional precision across humidity fluctuations—a critical factor for components with tight tolerances. This combination of thermal stability and low moisture absorption results in exceptional dimensional consistency in variable environmental conditions.
Among high-performance polymers, PPS stands out for its inherent flame retardancy. The material achieves UL94 V-0 flammability ratings without requiring additional flame retardant additives. Its molecular structure causes it to merely char during combustion rather than sustain a flame, enhancing safety in applications where fire resistance is critical.
Used in automotive and electrical components
Within the automotive sector, PPS has become invaluable for components exposed to high temperatures, chemicals, and mechanical stress. Primary applications include:
- Engine components including valve covers and thrust washers
- Fuel system components owing to resistance to all common automotive fuels
- Brake system parts requiring thermal stability
- Under-hood electrical connectors and housings
The electrical and electronics industry similarly benefits from PPS’s unique property profile. Its high dielectric strength coupled with thermal stability makes it ideal for:
- Electrical connectors and switches requiring reliability in harsh conditions
- Circuit boards for high-temperature applications
- Insulators and components for semiconductor manufacturing
- Electronic housings requiring both flame retardance and dimensional stability
PPS offers manufacturers a valuable alternative to more expensive high-performance polymers like PEEK for applications operating at moderate temperatures. Its exceptional hydrolytic stability—including resistance to hot water, steam, and high-pressure fluids—further expands its utility across diverse industrial settings.
Comparative Analysis of Top 5 Strongest Polymers
When evaluating the top five strongest polymers side by side, critical performance metrics reveal distinct advantages for specific applications. Engineers must carefully weigh these differences when selecting materials for high-stress industrial environments.
Strength-to-weight ratio comparison
The strength-to-weight ratio (specific strength) offers a critical metric for applications where weight reduction provides substantial benefits. Among high-performance polymers, this property varies considerably:
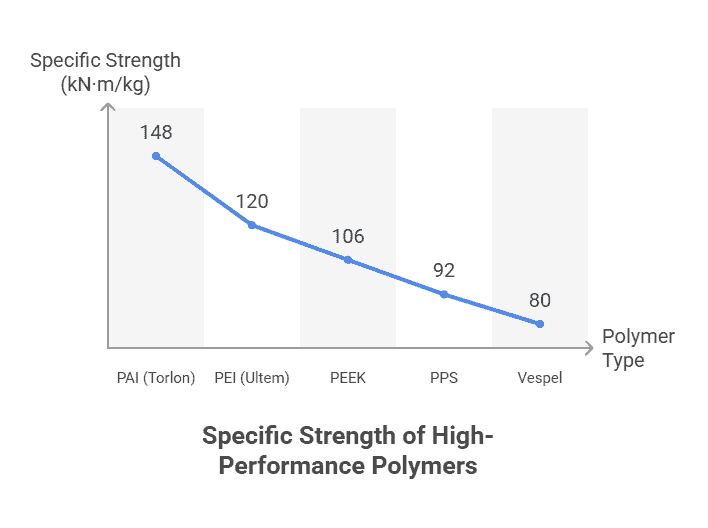
- PAI (Torlon): With tensile strength of 21,000 psi and density of 1.42 g/cm³, PAI offers the highest specific strength at approximately 148 kN·m/kg
- PEI (Ultem): Provides 15,200 psi strength with 1.27 g/cm³ density, yielding approximately 120 kN·m/kg
- PEEK: Delivers 14,000 psi strength with 1.32 g/cm³ density, resulting in approximately 106 kN·m/kg[371]
- PPS: Exhibits 12,500 psi strength with 1.36 g/cm³ density, providing approximately 92 kN·m/kg
- Vespel: Despite excellent thermal properties, its specific strength ranks slightly lower among these top five
Primarily, these strength-to-weight ratios exceed those of conventional polymers by factors of 3-5, making them suitable replacements for metal components in weight-critical applications.
Thermal and chemical resistance matrix
Chemical resistance varies substantially across these polymers, with environmental conditions dramatically affecting performance:
PEEK withstands continuous temperatures up to 260°C while maintaining excellent resistance to acids, bases, and hydrocarbons. Alternatively, Vespel operates reliably beyond 300°C—the highest among these materials—yet costs significantly more.
Hydrolytic stability demonstrates another critical difference; Ultem retains 85% of its tensile strength after 10,000 hours in boiling water, outperforming PEEK in this specific measure. Effectively, PPS offers the best overall chemical resistance, particularly against acids and bases, even surpassing PEEK in certain environments.
Maximize Performance with Engineered Polymers – Talk to an AIP expert about selecting and machining the strongest polymer for your demanding environment.
Creep resistance in polymers under load
Creep resistance—the ability to maintain dimensional stability under sustained load—represents a decisive factor for precision components. Temperature substantially impacts this property, with creep strain increasing by factors of 2.15-3.93 as temperatures rise from 20°C to 80°C.
Among these materials, Vespel demonstrates “outstanding creep resistance”, maintaining mechanical properties at continuous temperatures up to 500°F. Likewise, PAI exhibits “superior creep resistance”, making it particularly valuable for tight-tolerance applications.
The molecular structure fundamentally determines creep behavior—polymers with higher crystallinity (like PEEK and PPS) typically outperform amorphous polymers in creep resistance. Higher cross-linking density, typically found in PAI after post-curing, correspondingly enhances long-term dimensional stability under load.
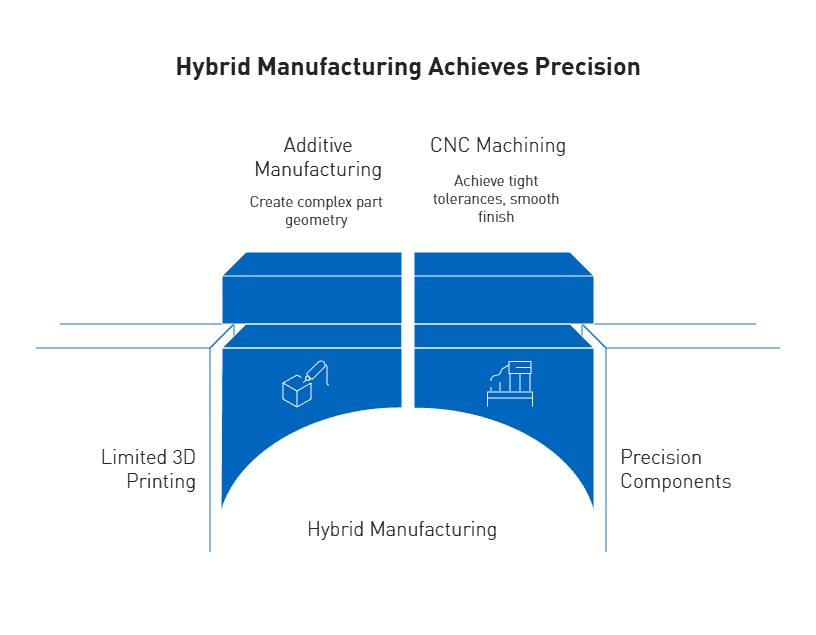
Machinability and Precision Part Considerations
CNC machining delivers precision components for mission-critical applications where high-performance polymers must withstand extreme pressures and stresses. Manufacturing these components involves careful consideration of material properties, machining parameters, and tolerance requirements.
High-pressure plastic components and tolerances
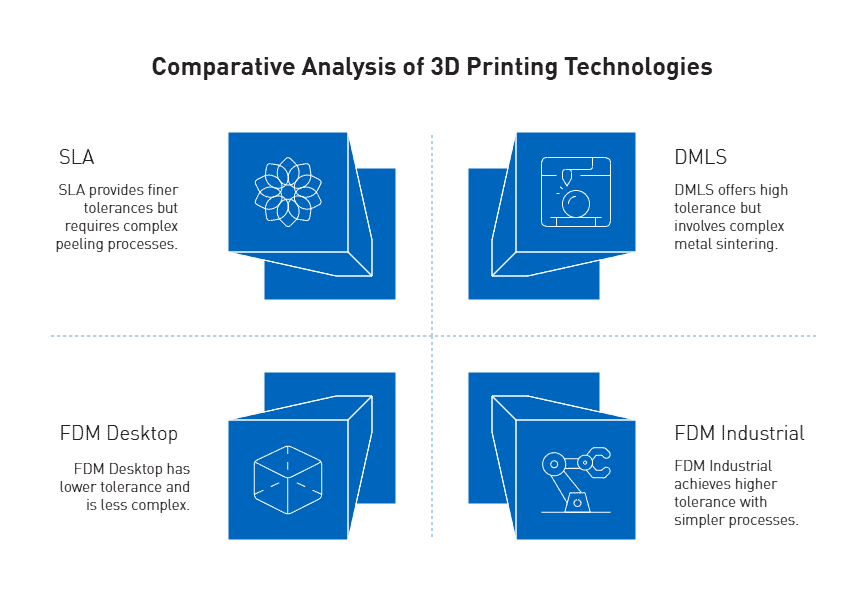
Manufacturing precision plastic parts demands strict adherence to tolerance specifications. Modern aerospace, medical, and defense applications frequently require components with tolerances as precise as ±0.001 inches. Primarily, the material choice significantly impacts achievable tolerances. Materials with low melt points present greater dimensional control challenges.
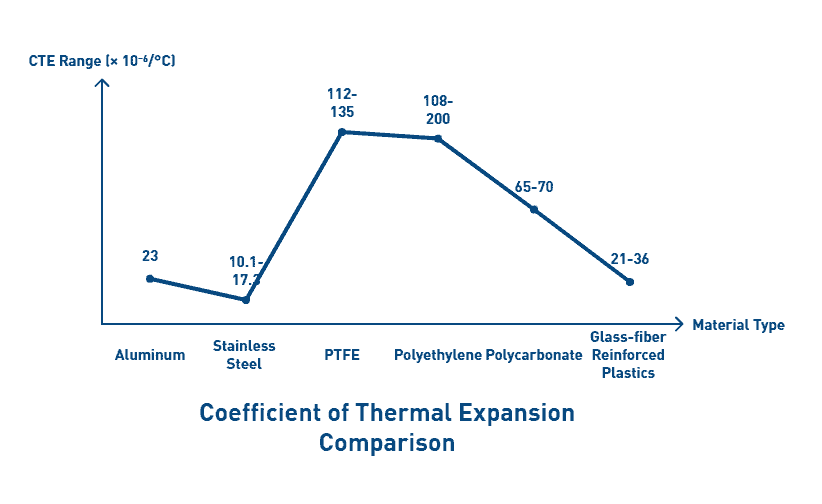
Temperature fluctuations critically affect dimensional stability due to polymer’s high coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). For instance, UHMW has a CTE of 0.0001 inch/degree, meaning a 10-foot piece can move 0.012 inches with just one degree temperature change. Henceforth, material selection must account for both operational conditions and manufacturing environment.
Machinable polymers for tight tolerances
Among high-performance polymers, achievable tolerances vary considerably:
- Acetal: ±0.001 inches
- PEEK: ±0.001 inches
- Nylon: ±0.002 inches
- PVC: ±0.002 inches
- UHMW/HDPE: ±0.005 inches
For optimal machining results, cutting parameters must be carefully controlled. Feed rates typically fall between 0.005 and 0.015 IPR, depending on material and cutting method. To circumvent heat buildup at the cutting interface, manufacturers employ sharp tools, moderate feeds, and high chip evacuation rates.
Fixturing techniques prove equally important. Since polymers are more elastic than metals, they become susceptible to deformation under excessive clamping pressure. In this case, customized fixtures providing support without excessive force yield better results.
How AIP Precision Machining supports material selection
With over 37 years of experience working with professionals across medical sciences, aerospace, defense, and specialized industrial sectors, AIP assists clients in navigating crucial material selection factors including:
- Electrical properties and dielectric requirements
- Mechanical strength and wear resistance
- Chemical exposure considerations
- Thermal stability requirements
- Industry-specific standards and regulations
In order to deliver optimal machined products, AIP employs state-of-the-art technology and maintains high quality standards throughout the manufacturing process, consistently achieving tight tolerances of ±0.001 inches or better.
Conclusion: Strategic Selection of High-Performance Polymers
Selecting the optimal polymer for demanding industrial applications requires thorough analysis of multiple performance factors beyond simple strength measurements. Throughout this examination of high-performance polymers, PAI (Torlon) clearly emerges as the strongest available option with its remarkable 21,000 psi tensile strength. Nevertheless, material selection decisions must consider application-specific requirements rather than relying solely on strength values.
Each polymer discussed offers distinct advantages for particular environments. PEEK delivers exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability up to 260°C, making it suitable for harsh chemical settings. Vespel stands out with superior creep resistance and thermal performance beyond 300°C, though at higher cost. Ultem provides an economical alternative with balanced properties and excellent dielectric strength. PPS offers outstanding chemical resistance with inherent flame retardancy at a moderate price point.
Engineers must consequently evaluate several critical factors when selecting materials:
- Mechanical requirements (tensile strength, compressive strength, modulus)
- Thermal stability needs (maximum continuous operating temperature)
- Chemical exposure conditions
- Creep resistance under sustained loads
- Dimensional stability requirements
- Cost constraints
Undoubtedly, the strength-to-weight ratio becomes particularly significant when weight reduction provides substantial benefits. PAI offers the highest specific strength at approximately 148 kN·m/kg, followed by PEI at 120 kN·m/kg and PEEK at 106 kN·m/kg. These values exceed conventional polymers by factors of 3-5, making them viable replacements for metal components in weight-critical applications.
Temperature significantly influences polymer performance, especially regarding creep behavior. As temperatures rise from 20°C to 80°C, creep strain increases dramatically, underscoring the importance of evaluating materials under actual operating conditions rather than relying solely on room-temperature data.
The manufacturing process additionally plays a crucial role in component performance. Precision machining capabilities must match the selected material’s properties to achieve required tolerances. Materials with higher dimensional stability generally allow for tighter tolerances during manufacturing.
Most importantly, engineers should approach polymer selection as a multi-dimensional decision process, considering the complete performance profile rather than focusing exclusively on strength values. This comprehensive approach ensures optimal material selection for critical industrial applications where failure is not an option.
For engineers tasked with selecting the strongest polymer for high-pressure, high-stress environments, working with a precision machining partner is essential. AIP Precision Machining brings over 40 years of specialized experience in high-performance thermoplastics, providing expert guidance in material selection and delivering components that meet the most demanding tolerance and performance requirements. Contact AIP today to discuss your application needs and ensure optimal performance through expertly machined polymer solutions.
FAQs
Q1. What is the strongest polymer available for industrial applications?
Polyamide-imide (PAI), also known as Torlon, is currently the strongest polymer available for industrial use. It has an exceptional tensile strength of 21,000 psi, making it ideal for demanding applications where high strength is critical.
Q2. How does PEEK compare to other high-performance polymers?
PEEK offers an excellent balance of properties, including high tensile strength (14,000 psi), thermal stability up to 480°F, and chemical resistance. While not as strong as PAI, PEEK outperforms many other polymers and is widely used in aerospace and oil & gas industries.
Q3. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a polymer for industrial use?
When selecting a polymer, consider mechanical properties (strength, stiffness), thermal stability, chemical resistance, creep behavior, dimensional stability, and cost. The specific requirements of your application should guide the selection process.
Q4. Which polymer offers the best combination of strength and cost-effectiveness?
Ultem (PEI) offers a good balance of strength (15,200 psi tensile strength) and cost-effectiveness. It’s often considered a more economical alternative to PEEK for applications that don’t require extreme temperature or chemical resistance.
Q5. How do high-performance polymers compare to metals in terms of strength-to-weight ratio?
High-performance polymers like PAI, PEI, and PEEK offer strength-to-weight ratios that exceed conventional materials by 3-5 times. This makes them excellent alternatives to metals in weight-critical applications, particularly in aerospace and automotive industries.