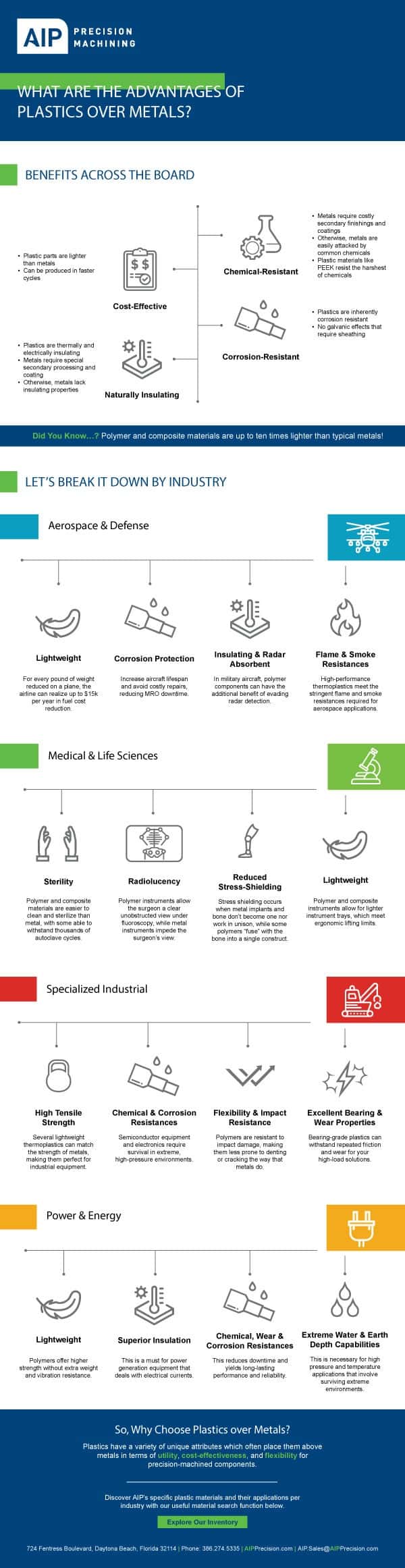
How Aluminum Got Dethroned by Thermoplastics in Aerospace
Cup holders. Magazines. Suit cases. Aircraft engines. Here’s a riddle, what do these items all have in common? If you’re an aircraft operator, the answer is obvious: they all add weight, making them a drain on your fuel costs.
If weight is one of the main operating costs of an aircraft, then it’s no surprise that airlines want to lose a few pounds. Over the last 36 years, AIP has witnessed firsthand the incredible weight savings that can be gained from using lightweight polymers and composites for aerospace applications.
How Airlines “Slim Down” Operating Costs
How much can an ounce cost you? Plenty. In the case of United Airlines, removing a single ounce from its in-flight magazine has translated to saving $290,000 a year. Yes, a single ounce can hit an airline with up to six digits in costs.
If thinner paper can have such an impact on your bottom line, then you can imagine the significant cost savings that can come from manufacturing lighter aerospace components. What’s the most lightweight solution for aircraft operators today? We have one word for you: plastics.
What Makes Plastics the Secret to Aircraft Fuel-Efficiency
Aluminum was popular during the “Golden Age of Aviation” because of its strength and durability as well as its lightness when compared to other metals like steel. As a result, many aircraft components have traditionally been metal, from aircraft interiors, to landing gear, aircraft engines and structural components.
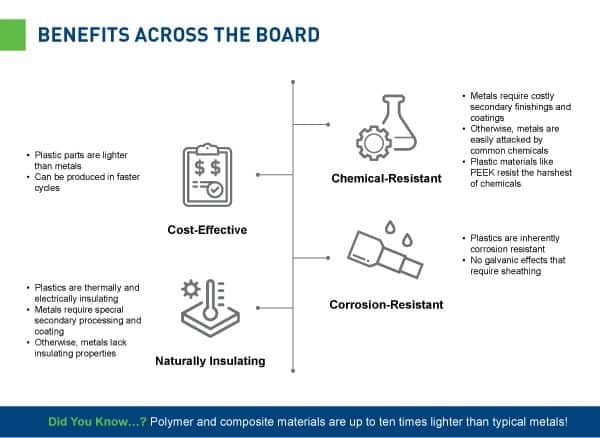
Now consider the fact that polymer and composite materials can be up to ten times lighter than metal. It’s no wonder that as more thermoplastic materials come on the market and new manufacturing opportunities arise, metal replacement has been seen as one of the best opportunities to reduce airline weight.
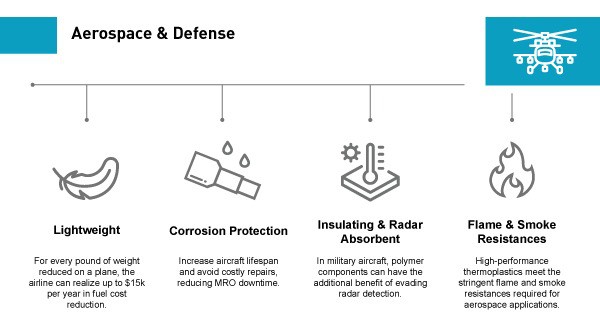
How big is the impact of switching from aluminum to plastic parts like PEEK and ULTEM in aerospace applications? Operators can earn weight savings of up to 60%. This translates to lower lifetime fuel costs, reduced emissions and extended flight range for operators.
“Weighing” the Option of Plastics in Aerospace
Weight alone is a massive reason to consider thermoplastics for aerospace, but weight isn’t the only factor at play in material selection.
After all, wood is lighter than metal, but there’s a reason we don’t build spruce airframes like the first plane from the Wright brothers: it wouldn’t be safe today to fly a wooden plane! Aerospace components need to be able to survive in corrosive, harsh environments as well as provide resistance to high temperatures.
In other words, it’s crucial that your mission-critical components aren’t just lightweight, but also high-performing.
At AIP, we carefully apply our decades of material expertise to select the right material for your application’s needs. Remember that your aerospace plastics manufacturer should understand the unique demands of your industry and your application, and have experience machining the material you require.
Want to learn more about how AIP reduces costs for aircraft operators?
Read how machined polymer components can take a load off aircraft interiors in our aerospace case study.
Download our Case Study |










 With 36+ years of experience in the industry, our dedicated craftsmen and ties to leading plastic manufacturers allow us to provide you with unrivaled knowledge and consulting in material selection, sizing, manufacturing techniques and beyond to best meet your project needs.
With 36+ years of experience in the industry, our dedicated craftsmen and ties to leading plastic manufacturers allow us to provide you with unrivaled knowledge and consulting in material selection, sizing, manufacturing techniques and beyond to best meet your project needs.