An Informational Brief on Polymer Machining
Polybutylene Terephthalate, also known as PBT, is a crystalline polyester thermoplastic that is a household name in everyday applications. You can find it under the hood in automotive applications, such as brake cable liners or sockets due to its ability to endure harsh environments and resist chemicals. In food processing and electrical applications, it is chosen for its resistance to staining and low moisture absorption. As industries continue to expand and populations grow, the demand for this thermoplastic “miracle worker” only continues to increase.
AIP has over 37 years of experience machining complex components from thermoplastics like Polybutylene Terephthalate. In this insightful technical brief, we will discuss what goes into machining PBT and how it differs from other manufacturing options such as metal machining, injection molding, and 3D printing.
Properties of PBT
It is beneficial to keep information on the properties of a thermoplastic pre-machining. This helps in selecting the right thermoplastic for a project. Furthermore, it assists in evaluating if the end use requirement would be fulfilled or not. Below are some of the key characteristics of Polybutylene Terephthalate:
PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) is a thermoplastic polyester that is very similar to PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) but has a slightly better impact resistance. As a semi-crystalline engineering thermoplastic, it has outstanding processing properties for molding, thermoforming and machining. It is often a prime candidate for injection molding as the material crystallizes rapidly, so mold cycles are short and temperatures can be lower than for many thermoplastics.
PBT is produced by polycondensation of terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate with 1,4-butanediol using special catalysts.
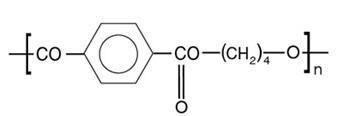
Molecular Structure of PBT
Chemical Formula: (C12H12O4)n
Key features of Polybutylene Terephthalate
PBT displays excellent mechanical and electrical properties like good chemical resistance, impact resistance, low moisture absorption, rigidity, low co-efficient of friction and staining resistance. It is often reinforced with glass-fibers or minerals to improve its tensile, flexural and compressive strengths and moduli.
| Material Property | Value |
| Elongation at Break | 5-300% |
| Elongation at Yield | 3.5-9% |
| Flexibility & Stiffness (Flexural Modulus) | 2-4 GPa |
| Hardness Rockwell M | 70-90 |
| Hardness Shore D | 90-95 |
| Tensile Strength | 40-50 MPa |
| Notched Izod Impact at Room Temperature | 27-999 J/m |
| Notched Izod Impact at Low Temperature | 27-120 J/m |
| Young Modulus | 2-3 GPa |
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion | 6-10 x 10-5/oC |
| Shrinkage | 0.5-2.2% |
| Water Absorption 24 hours | 0.1-0.2% |
Applications of PBT
PBT finds many applications in the electrical and automotive industries. It is particularly common in food processing applications as it offers very low moisture absorption, resistance to staining and resistance to cleaning chemicals.
At room temperature, PBT is resistant to the following chemicals: aliphatic hydrocarbons, gasoline, carbon tetrachloride, perchloroethylene, oils, fats, alcohols, glycols, esters, ethers and dilute acids and bases. However, they are attacked by strong bases.
For this reason, PBT can endure extreme and harsh environments such as automotive under-hood applications, outdoor electrical applications where fire is a concern, and valves or insulation in food processing or autoclave components.
Other common applications include:
- Cams
- Food Piston Pumps
- Fuel Pump Components
- Gears
- Wear Strips
- Housing Components
The broad use of PBT is also shown by the numerous regulatory approvals held by various grades. These include VDE or UL-approvals for the electrical and electronics market or FDA approval for the nutrition and medical market.
Grades of PBT
At AIP, we machine various grades and brand name Polybutylene Terephthalate, including Hydex PBT. Branded names include the following:
- CELANEX
- DURANEX
- HYDEX 4101
- HYDEX 4101L**
- SUSTADUR PBT
- TECADUR
- VALOX
- TECADUR PBT GF30
**PBT is also available as Hydex 4101L in a bearing grade.
Our close ties with the industry’s leading plastics manufacturers give us even further insight and access to technical help in material selection, sizing and manufacturing procedures. Whatever your application, our machinists can help you in material selection, sizing and manufacturing techniques from concept to completion.
Machining PBT
Annealing PBT
Annealing and stress-relieving plastics is crucial to the machining process. If not machined with coolants, lubricants and trained procedures, this material is subject to cracking and crazing. The annealing process at AIP greatly reduces the chances of these stresses occurring from the heat generated during machining polymers like PBT. Our machinists use computer controlled annealing ovens for the highest quality precision temperatures and time control.
Machining PBT
We recommend non-aromatic, water-soluble coolants because they are most suitable for ideal surface finishes and close tolerances. These include pressurized air and spray mists. Coolants have the additional benefit of extending tool life as well.
PBT is a semi-aromatic thermoplastic that is easily molded and thermoformed. Since it crystallizes rapidly, mold cycles are short and molding temperatures can be lower compared to other engineering plastics.
Some companies machine both metals and plastics, which has detrimental outcomes for machined polymer products. Many past experiences have shown parts going to customer without cracks, only to develop surface cracks and warping over time due to exposure to metal machine shop fluids. Be sure to use a facility like AIP that only machines polymers.
Preventing Contamination
Contamination is a serious concern when machining polymer components for technically demanding industries such as aerospace and medical sciences. To ensure the highest level of sanitation down to the sub-molecular level, AIP Precision Machining designs, heat-treats, and machines only plastics with any sub-manufactured metalwork processed outside our facility. This allows us to de-risk the process from metallic cross contamination.
Polybutylene Terephthalate Machining Guide: Supportive Information
General Engineering Materials
Quality Assurance Certifications
Providing unrivaled expertise and unparalleled results is at the heart of our mission at AIP Precision Machining.
Tell us about your project’s specifications and we will help you solve your plastics puzzle.