The global surgical robots market, valued at $3.92 billion, is estimated to reach $7.42 billion by 2030. Precision machined components for orthopedic navigation devices serve as the foundation for this rapidly expanding field, enabling surgeons to achieve remarkable levels of accuracy during complex procedures.
Robotic systems are transforming orthopedic surgery by facilitating new approaches. These advanced navigation systems combine cutting-edge technologies and provide real-time guidance during surgeries, significantly enhancing a surgeon’s ability to perform complex maneuvers with exceptional precision. Specifically, in minimally invasive surgery-transforaminal interbody fusion procedures, orthopedic surgical robots enhance accuracy compared to traditional freehand techniques, with a 2021 review showing robotic accuracy ranging from 94.6% to 99%. These impressive results highlight why precision machined components play such a critical role in the development and functionality of orthopedic navigation devices that continue to advance surgical capabilities.
Precision Machining Techniques for Orthopedic Navigation Systems
Modern orthopedic navigation technology requires manufacturing techniques that can consistently deliver components meeting the highest standards.
Multi-axis CNC Milling for Surgical Navigation Housings
Advanced 5-axis CNC milling represents a crucial innovation for navigation system housings, enabling the creation of complex geometries that would be impossible with traditional methods. Unlike standard 3-axis machining, 5-axis capability adds two rotational axes that allow for complex contours and multi-surface machining in a single setup. This technology proves essential for navigation housings that must precisely contain sensors while maintaining biocompatibility and sterilizability. Moreover, these systems can achieve exceptional dimensional accuracy—often within ±0.002 mm—crucial for components that interface with human anatomy.
Live Tooling for Complex PSU and PPSU Geometries
Live tooling technology enhances the capabilities of CNC lathes, enabling milling operations on the same machine—ideal for producing small, complex orthopedic components with high precision. For PPSU (polyphenylsulfone) components commonly used in navigation instruments, this approach proves particularly valuable. PPSU materials are selected specifically when repeated steam sterilization is required, necessitating specialized machining strategies that preserve the material’s beneficial properties. Consequently, this integrated approach reduces setups and maintains tighter tolerances.
Surface Finishing for Biocompatible Thermoplastics
Surface quality directly impacts biocompatibility in medical components. Key aspects affecting biocompatibility include surface roughness, surface features, chemistry, crystallinity, and porosity. For navigation systems, finishing techniques create surfaces that minimize bacterial colonization while optimizing sensor function. Indeed, skilled machining centers can achieve surface roughness readings as low as Ra < 0.02 μm, essential for articulating surfaces and device interfaces.
Tolerancing Requirements for Navigation-Grade Components
Navigation systems demand exceptionally tight tolerances to ensure accurate positioning on patient anatomy. For critical interfaces and alignment features, typical tolerance targets range from ±0.02–0.05 mm, depending on material properties. Profile tolerancing, rather than linear dimensioning, often provides advantages in quality control for complex navigation components, reducing inspection time while maintaining precision. This approach addresses the unique challenges of thermoplastic components that must interface precisely with both sensors and surgical instrumentation.
High-Performance Polymers in Navigation-Enabled Devices
High-performance polymers form the backbone of modern orthopedic navigation systems, offering unique properties that enhance surgical precision and patient outcomes. These advanced materials enable the creation of lightweight, durable, and functionally superior components essential for navigation-enabled devices.
ULTEM™ Machined Parts for Radiolucent Applications
ULTEM™ (polyetherimide or PEI) stands out as an exceptional material for navigation components requiring transparency to imaging technologies. This amber-colored polymer combines high strength and rigidity at elevated temperatures with exceptional dimensional stability. Most importantly, ULTEM™ retains 100% of its tensile strength even after 2,000 steam autoclave cycles at 270°F, making it ideal for reusable navigation instruments. The polymer’s inherent radiolucency allows unobstructed visualization during image-guided procedures, a critical requirement for orthopedic navigation. For applications demanding additional rigidity, glass-filled ULTEM™ versions provide enhanced dimensional stability while maintaining the material’s valuable radiolucent properties.
PEEK and CFR-PEEK in Sensor-Compatible Housings
PEEK (polyetheretherketone) and its carbon-fiber-reinforced variant (CFR-PEEK) have revolutionized sensor housing design in navigation systems. These materials offer mechanical properties remarkably similar to cortical bone, thereby reducing stress shielding. Their radiolucency enables clear post-operative imaging without interference, a crucial advantage over metal components. Notably, PEEK-based materials have been implanted in approximately 15 million devices worldwide with zero material-related recalls, demonstrating exceptional reliability. Additionally, CFR-PEEK can support directly printed sensors on its matrix, creating new possibilities for designing sensor functions targeting different orthopedic applications.
PPSU for Sterilizable Surgical Navigation Tools
Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU) delivers superior performance among sulfone polymers for navigation instruments that require repeated sterilization. This high-performance material offers impact strength similar to polycarbonate but with enhanced chemical resistance and operating temperatures around 200°C (392°F). PPSU maintains its mechanical properties through 800 sterilization cycles and shows no significant discoloration even after 1,000 cycles. For enhanced visibility during procedures, specialized PPSU variants like TECASON P MT XRO incorporate contrast media that enable clear visualization under fluoroscopy and X-ray, making it ideal for orthopedic navigation tools.
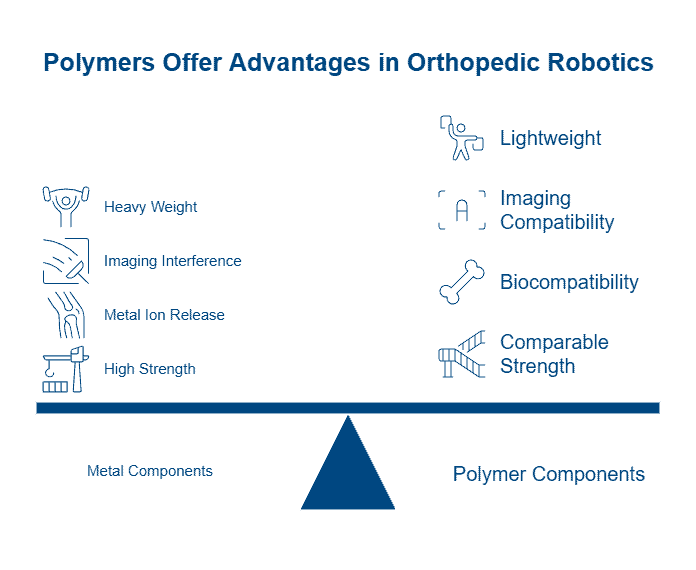
Polymer Replacement for Metal in Orthopedic Robotics
High-performance polymers increasingly replace metals in robotic orthopedic applications, offering several advantages:
- Weight reduction: Components can be up to 70% lighter than traditional metal versions
- Imaging compatibility: Radiotransparent polymers allow unobstructed intraoperative visualization
- Biocompatibility: Materials avoid metal ion release that can cause osteolysis
- Mechanical performance: Advanced polymers maintain strength comparable to metals
In robotic surgical systems, these polymers are used in mechanical arms, connections between tools, and housings. Specialty polymers like PPSU, PEEK, and reinforced PARA compounds enable greater design freedom while withstanding harsh cleaning environments necessary for surgical applications.
Quality and Compliance in Precision Polymer Machining
Quality management serves as the cornerstone for manufacturers creating precision components for orthopedic navigation systems. Stringent standards ensure these critical devices perform safely and effectively in surgical settings.
ISO 13485 Certification for Navigation Component Manufacturing
ISO 13485 certification establishes a comprehensive quality management system specifically designed for medical device manufacturing. This internationally recognized standard requires detailed documentation of all manufacturing processes, from raw material inspection to final product testing. Essentially, certification demonstrates to regulators that manufacturers meet stringent requirements for safety and quality.
FDA-Compliant Plastic Parts for Surgical Use
Adherence to FDA regulations, including Title 21 CFR which outlines rules for medical devices, ensures plastic components meet necessary safety standards. Manufacturers must comply with quality system regulation (Part 820), establishment registration (Part 807), and unique device identification (Part 830). These requirements help maintain the highest levels of safety and efficacy in orthopedic navigation tools.
Traceability and Lot Control in Navigation Systems
Traceability enables tracking of components throughout their lifecycle—from procurement and use to sterilization and final disposition. Each implant requires a lot control identifier, allowing manufacturers to trace individual items during their transactional journey. This capability proves essential for ensuring safety, meeting compliance requirements, and enabling efficient recalls when needed.
Cleanroom Machining Standards for Implantable Devices
Cleanroom facilities maintain stringent cleanliness levels by controlling air pollutants such as dust, microbes, and particulates. Medical device manufacturing cleanrooms typically meet at least ISO-8 classification, with a maximum particle count of 100,000 per cubic foot. Proper HEPA filtration systems, controlled airflow, and strict protocols ensure component quality and patient safety.
Integration of Machined Components in Robotic Orthopedic Surgery
Robotic orthopedic surgery relies on precision machined components that seamlessly integrate with navigation systems for optimal performance. These components must function cohesively within complex assemblies to deliver the accuracy surgeons require.
Component Fitment in Robotic Arms and End Effectors
Robotic arms in orthopedic surgery provide unprecedented precision, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced control. The robotic components can rotate 360 degrees, offering range of motion beyond human capabilities. Critical to this functionality is the integration of precision-machined instruments with multiple articulating joints that mimic human finger movements. In settings where optical alignment faces line-of-sight blockages, inertial-guided surgical tools can supplement or replace optical guidance.
Precision Interfaces for Sensor Mounting in Navigation Tools
Inertial navigation systems incorporate Kalman filters—technology first used in Apollo moon missions—to merge data from multiple sensors, providing accurate location estimates. These systems help align artificial joints according to patient-specific characteristics. Properly calibrated sensor interfaces ensure that transition matrices between the robotic unit and CAD models align precisely with physical components. Subsequently, this precision helps counter surgeon hand tremor and fatigue.
Role of AIP Precision in Robotic Surgical Instrumentation
High-definition 3D visualization systems capture detailed images of surgical sites, enabling unparalleled accuracy. Hence, the precision components manufactured for these systems must maintain tolerances typically within 0.2mm. Robotic milling offers advantages over traditional CNC machining, primarily through reduced manufacturing time and costs.
Conclusion
Precision machined components serve as the foundation for advanced orthopedic navigation systems that continue to improve surgical outcomes. The integration of multi-axis CNC milling, live tooling, and specialized surface finishing techniques allows for components that meet the exacting tolerances required for navigation-grade applications.
Materials like ULTEM™, PEEK, CFR-PEEK, and PPSU offer significant advantages over traditional metals, including radiolucency, sterilizability, and mechanical properties that closely mimic biological structures. These characteristics make them ideal for sensor housings, navigation tools, and robotic components that must function flawlessly during critical procedures.
Quality management systems remain non-negotiable for manufacturers working in this space. ISO 13485 certification, FDA compliance, rigorous traceability protocols, and cleanroom manufacturing environments ensure components meet the highest standards for safety and effectiveness. Subsequently, these quality measures build confidence among surgeons and patients alike.
The future of orthopedic surgery will undoubtedly depend on continuous advancement in precision machined components. Robotic systems equipped with these components already demonstrate impressive accuracy rates exceeding 94% in complex procedures. Patients benefit from shorter recovery times, reduced complications, and improved long-term outcomes due to the precise alignment and placement these navigation systems facilitate.
Additionally, the shift toward high-performance polymers creates new possibilities for innovative designs that were previously impossible with traditional materials. Engineers can now develop lighter, more ergonomic tools that enhance surgeon control while maintaining the strength and durability necessary for repeated use.
This convergence of precision machining, advanced materials, and robotic technology represents a significant leap forward in orthopedic surgery. Though challenges remain in scaling production and reducing costs, the trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated navigation systems becoming standard practice across a broader range of orthopedic procedures. Patients worldwide will ultimately benefit from the enhanced precision these machined components enable in the operating room.
At AIP Precision Machining, we specialize in delivering mission-critical components for orthopedic navigation systems that demand uncompromising accuracy, biocompatibility, and sterilization performance. Whether you’re developing next-generation robotic platforms or improving existing surgical instrumentation, our team offers ISO 13485-certified expertise in high-performance polymer machining to support your goals.
Contact us today to discuss how AIP can support your next orthopedic navigation project.
FAQs
Q1. What are precision machined components in orthopedic navigation?
Precision machined components in orthopedic navigation are highly accurate parts manufactured using advanced techniques like multi-axis CNC milling and live tooling. These components, often made from high-performance polymers, are crucial for creating surgical navigation systems that require exceptional dimensional accuracy and biocompatibility.
Q2. How do high-performance polymers benefit orthopedic navigation devices?
High-performance polymers like ULTEM™, PEEK, and PPSU offer numerous advantages in orthopedic navigation devices. They are radiolucent, allowing for clear imaging during procedures, can withstand repeated sterilization, and have mechanical properties similar to bone. These materials enable the creation of lightweight, durable, and functionally superior components essential for navigation-enabled devices.
Q3. What quality standards are important for manufacturing orthopedic navigation components?
Key quality standards for orthopedic navigation components include ISO 13485 certification, FDA compliance, and adherence to cleanroom machining standards. These ensure that components meet stringent safety and effectiveness requirements, maintain traceability throughout their lifecycle, and are manufactured in controlled environments to prevent contamination.
Q4. How are precision machined components integrated into robotic orthopedic surgery?
Precision machined components are integrated into robotic arms, end effectors, and navigation tools in orthopedic surgery. They enable the creation of complex articulating joints, precise sensor interfaces, and high-definition visualization systems. These components work together to provide surgeons with enhanced control and accuracy during procedures.
Q5. What are the benefits of using precision machined components in orthopedic navigation?
Using precision machined components in orthopedic navigation leads to improved surgical outcomes, including increased accuracy in bone cutting and component alignment, reduced operative time, and enhanced patient satisfaction. These components enable navigation systems to achieve remarkable levels of precision, with some studies showing accuracy rates exceeding 94% in complex procedures.